- Details
- Hits: 3439
Railroad: Wabash railroad
The Wabash railroad was created in 1881 to consolidate the Detroit, Butler & St. Louis in Michigan and other lines in the midwest and southern Ontario, Canada. In Michigan, it owned 76 miles of rail between Delray and the Ohio State Line (near Morenci). It had 44.23 miles of spurs and sidings in Michigan.
This line leased the Detroit Union Depot and Terminal Association tracks and Union Depot to Delray (4.06 miles). It also leased use of the Ann Arbor Railroad from Milan to the Ohio State line (25.2 miles) giving it a route to Toledo from the north.
The railroad was reorganized several times and became the owner of the Ann Arbor and DT&I railroads for a time. In 1964, the Wabash was purchased by Norfolk & Western and later combined into the Norfolk Southern railroad. This railroad was also part of the partnership of the Union Belt of Detroit.
For use of trackage from West Detroit to the Detroit stock yards, the Wabash bills the GT each way as follows: Engines 90¢, loads 30¢, empties 15¢, cabooses 30¢ per agreement dates January 16, 1922. For GT trackage between West Detroit to Beaubien Street, Wabash bills GT for trackage each was as follows: Engines 90¢, loads 30¢, empties 15¢, and cabooses 30¢. [GT memorandum 1935]
Detroit, St. Louis & Western → Wabash Railroad → Norfolk & Western
Operated in Michigan: 72 years.
Chartered in: 1889
Consolidated: 1889 - Detroit, State Line & Wabash; Wabash Western; and other non-Michigan companies. Also leased the Detroit Union Railroad Depot & Station; and joint control with others of the Fort Street Union Depot.
Control: 1925 - of the Ann Arbor Railroad.
Control: 1928 - by the Pennsylvania Railroad.
Leased: 1961 - to the Norfolk & Western. PRR relinquished control to the N&W in 1970.
Control: 1963 - of the Ann Arbor Railroad turned over to the Detroit, Toledo & Ironton.
Reference: [MRRC]
 Notes
Notes
The Wabash Railroad started with a construction railroad known as the Detroit, State Line & Wabash, and eventually extended from Buffalo, NY on the east, through southern Ontario, Canada, and then from Detroit to St. Louis, MO. The railroad had other important branches from Toledo to Chicago, and from Chicago southwest.
Car ferry operations transported rail cars over the Detroit river from a port near the Fort Street Union Station (on the jointly owned Union Belt of Detroit). The Wabash's main locomotive roundhouse was just east of Delray on the Union Belt, and their main freight yard was Manifest Yard in what is today known as Melvindale, west of the Rouge River.
The Wabash was merged into the Norfolk & Western Railway in 1964.
Time Line
1881. The railroad begins friendly connections with the Grand Trunk at Grand Trunk Junction (West Detroit), in part as a result of the Vanderbilt road's interference with the GT establishing its own cross-Michigan route. [GTWHS-2020-Sum]
1883. March 18. Began using the Fort Street Union Depot. [GTWHS-2020-Sum]
1903. Henry K. McHarg of New York was a director of the Wabash, and he also owned the Detroit & Mackinac railroad. This set off speculation that the D&M would become part of the Wabash, which was not practical and did not happen. [MCR-1904]
1903. SNAPSHOT. The Wabash operated 32 stations in Michigan (out of a total of 725 stations). The five top categories of freight carried (by ton) were: coal (30%); miscellaneous commodities (15%); grain (14%); lumber (5%); and merchandise (6%). They owned 534 locomotives (system), and several thousand cars.
1920. The Wabash railroad serves 48 industries in Detroit with 42 sidings and a car capacity of 453 cars. They have 5 sets of team tracks which hold 156 cars and four freight houses. [DWT-1920]
1926. October 23. The Wabash awards a contract to build a second main line track from Lima Junction, OH to Britton, MI, 21.6 miles. [RR]
1928. The Pennsylvania railroad acquires substantial stock in the Wabash but the ICC does not allow them to take control. [TSD]
1930. The Pennsylvania railroad is ordered to relinquish control of the Wabash railroad. [ENR-1930-1211:941]
Maps
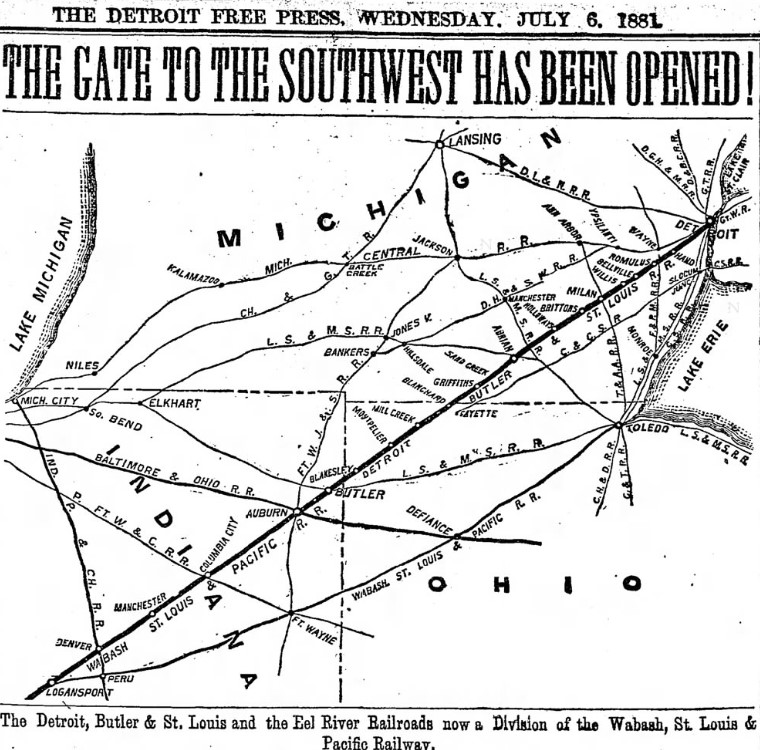
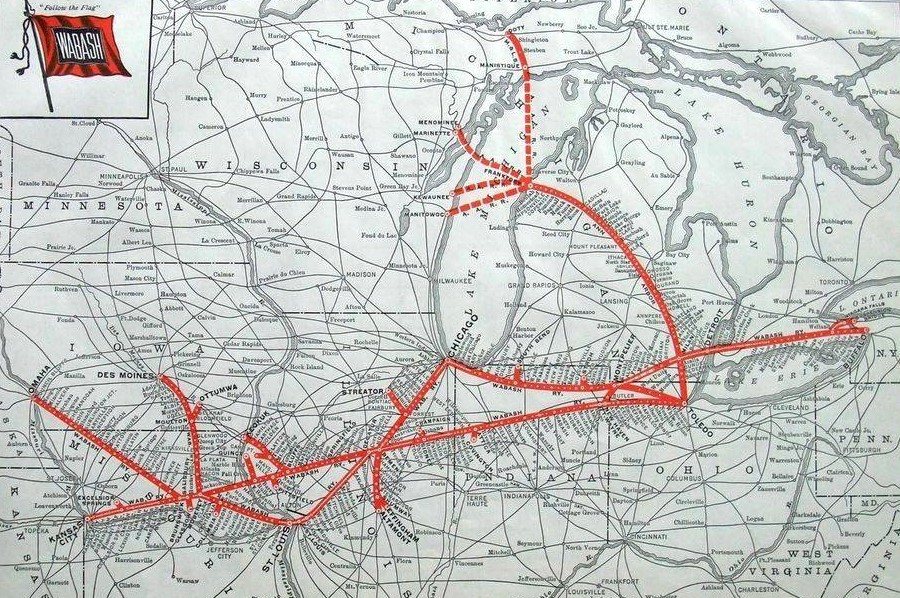
Image info: Top, the opening of the Detroit, Butler and St. Louis railroad to Detroit, in 1881. [DFP-1881-0706]. 2nd map, a system map of the Wabash railroad, the successor to the DB&StL.
Bibliography
The following sources are utilized in this website. [SOURCE-YEAR-MMDD-PG]:
- [AAB| = All Aboard!, by Willis Dunbar, Eerdmans Publishing, Grand Rapids ©1969.
- [AAN] = Alpena Argus newspaper.
- [AARQJ] = American Association of Railroads Quiz Jr. pamphlet. © 1956
- [AATHA] = Ann Arbor Railroad Technical and Historical Association newsletter "The Double A"
- [AB] = Information provided at Michigan History Conference from Andrew Bailey, Port Huron, MI

