- Details
- Hits: 5070
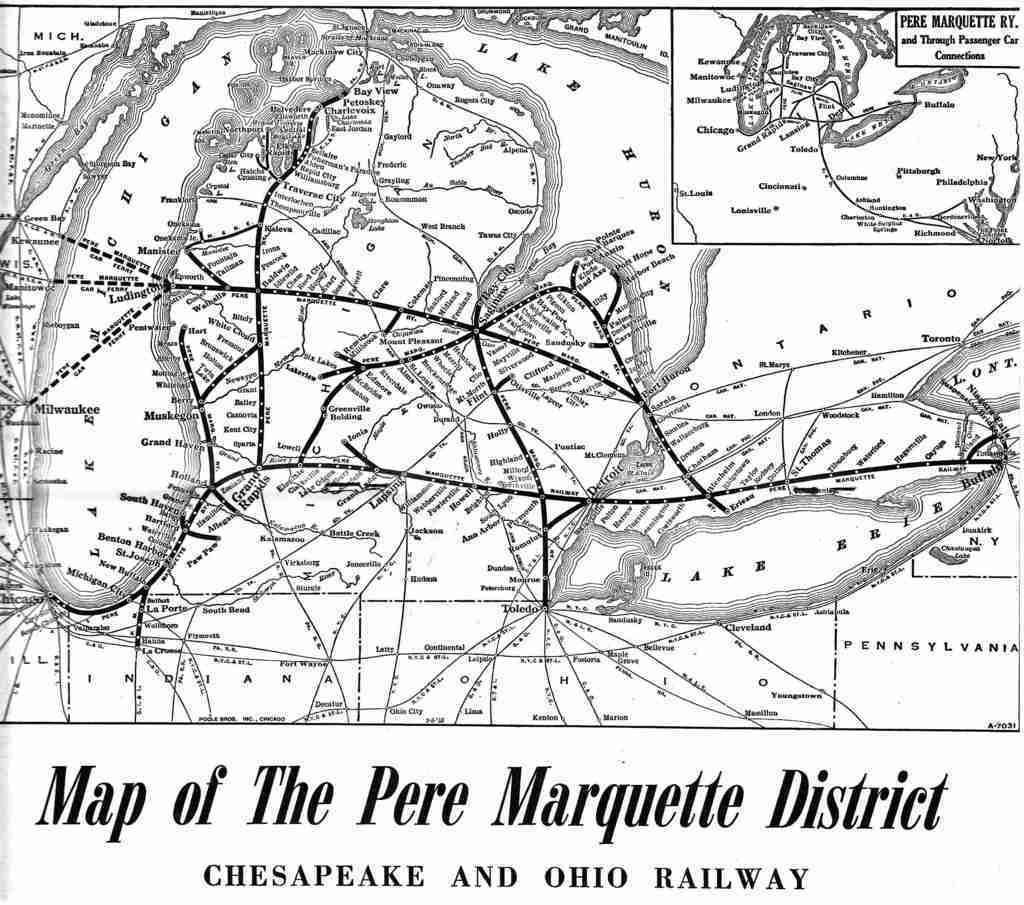
Railroad: Pere Marquette railroad
The Pere Marquette Railroad was formed in 1900 to consolidate the Flint & Pere Marquette, the Detroit, Grand Rapids and Western railroad, the Chicago & West Michigan railway, and other smaller lines and branches throughout the lower peninsula of Michigan and into Ontario, Canada.
Various (see below) → Pere Marquette Railroad → Chesapeake & Ohio railroad
Incorporated: 1899 - by Flint & Pere Marquette, Detroit Grand Haven & Western and Chicago & West Michigan.
Operated: 47 Years
Consolidated: 1899 - Above three lines and others between 1900 and 1939.
Controlled by: Frederick H. Prince syndicate, Boston, Mass.
Control of: 1907 - by Cincinnati, Hamilton & Dayton. Ended in 1912.
Control by: 1929 - by Chesapeake & Ohio railroad.
Merged: 1946 - into Chesapeake & Ohio railroad.
Reference: [MRRC]
Notes
The company was reorganized in 1917 by the owners of the Chesapeake & Ohio. The PM merged with the C&O in 1947 and over time the name "Pere Marquette" disappeared to become the C&O, Chessie System, and later CSX.
Books
Pere Marquette: A Michigan Railroad System before 1900, by Graydon Meints, by Graydon Meints
Videos
Old Pere Marquette video in Detroit and Michigan from the 1940's.
1940's PMRR footage of yard engines at Ottawa Yard, Erie, MI
Map
Time Line
1903. November. PM reaches a deal with Vanderbilt lines to enter both Buffalo and Chicago. [NYT-1903-1126:4-4]
1903. SNAPSHOT: The PM had 1,972 miles of track in Michigan, Indiana and the Toledo, Ohio area. They operated 15 drawbridges, 315 stations, employed 6,950 people in Michigan including 337 engineers, 350 firemen, 225 conductors, 452 brakemen, 76 baggagemen, 281 laborers, 745 shopmen, 270 yardmen and 4,339 others. They operated 269 locomotives, 22 120-wheel passenger cars, 209 8-wheel passenger cars, 57 baggage/express cars, 4,367 box cars, 83 stock cars, 2,331 platform cars, 948 ballast cars, 116 conductors' way cars. The top five categories of freight hauled (by tonnage) was: 25% bituminous coal, 14% lumber, 11% miscellaneous commodities., 9% logs and 4% grain. MCR-1904]
1903. December 26. A collision on the Pere Marquette at East Paris kills 18. This was a head on collision caused by a misreading of train orders. The railroad had 20 employees killed this year, along with 199 injured in various mishaps. [MCR-1904]
1904. May 1. PM line into Buffalo, NY is formally opened for freight and passenger service. [RA-1904-0429:878]
1904: June. Pere Marquette makes arrangements with the Toledo Belt Line for use of its property. [RG-1904-0624:8]
1904: August. The PM apparently merges or comes under the control of the Cincinnati, Hamilton & Dayton railroad. [RA-1904-0805:193]
1908. February. H. B. Ledyard, the chairman of the Michigan Central railroad is elected as a Pere Marquette director. [RA-1908-0207:198]
1920. The Pere Marquette railroad serves 64 industries in Detroit with 68 sidings and a car capacity of 841 cars. They have 12 sets of team tracks which hold 311 cars and two freight houses. [DWT-1920]
1921. September. The PM is authorized to acquire control of the Flint Belt railroad. [RR-1921-0910:348]
1921. The seventh annual inspection train of the Pere Marquette railway left Petoskey on the third day of a nine day tour of the entire system. The inspection is made annually in order to make ready for the usual winter operations, which are generally difficult in January and February. The train carrying the party consists of three office cars, a Pullman, a diner and a specially constructed inspection car.
The entire 2,206 miles will be covered before the party disbands at Plymouth Saturday noon next. President Frank H. Alfred is on the train along with about a dozen other officials. From Grand Rapids, the train runs through to Detroit and crosses over to Windsor. [TCRE-1921-1024]
1926. March 6. The planned merger of the Pere Marquette and the Nickel Plate Road was disapproved by the ICC. [RR]
1926. April. PM orders 350 automobile box cars. [RR-1926-0410:698]
1926. July. PM accepts terms for inclusion in a merger with the Nickel Plate under the Van Sweringen plan. [RR-196-0731:182]
Bibliography
The following sources are utilized in this website. [SOURCE-YEAR-MMDD-PG]:
- [AAB| = All Aboard!, by Willis Dunbar, Eerdmans Publishing, Grand Rapids ©1969.
- [AAN] = Alpena Argus newspaper.
- [AARQJ] = American Association of Railroads Quiz Jr. pamphlet. © 1956
- [AATHA] = Ann Arbor Railroad Technical and Historical Association newsletter "The Double A"
- [AB] = Information provided at Michigan History Conference from Andrew Bailey, Port Huron, MI